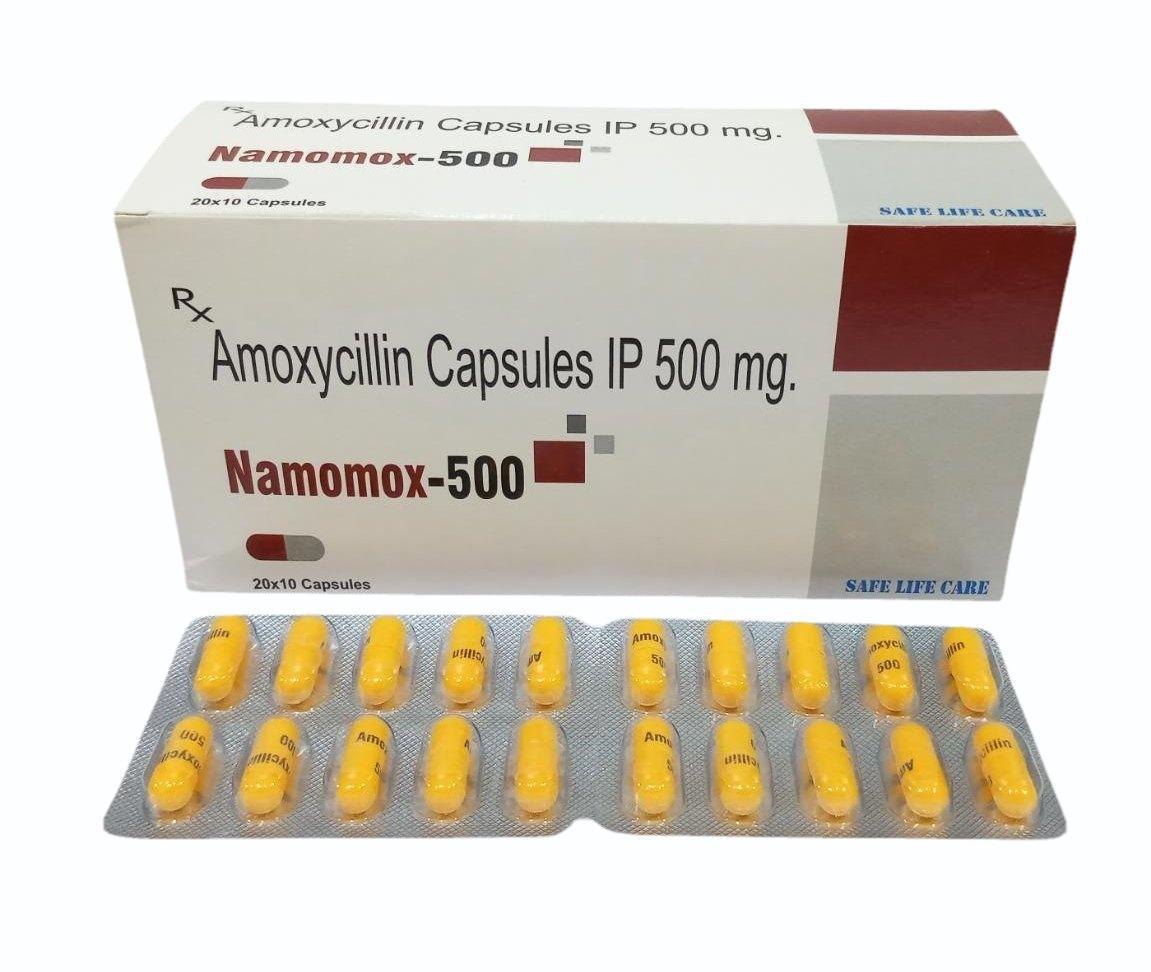
AMOXICILLIN is a widely-used antibiotic drug. It belongs to the penicillin group of drugs and is used to treat certain infections that are caused by bacteria. Amoxicillin fights bacteria and stops them from growing by preventing them from forming cell walls. This kills the bacteria and eventually eradicates the infection.
USES
Bronchitis.
Ear Infection.
Gonorrhea.
Lyme Disease.
Pneumonia.
Skin Infections.
Throat Infections.
Tonsillitis, Typhoid, Urinary Tract Infections.
GUARANTEE
Original generic from various Indian pharmaceutical companies. Photos of the product are for illustration purpose only and may vary according to the manufacturer.
DESCRIPTION
Amoxicillin can be used in combination with another antibiotic called clarithromycin to treat stomach ulcers caused by H. pylori bacterial infection. These drugs can also be combined with lansoprazole to help reduce stomach acid and symptoms of acid reflux. Health care providers sometimes prescribe amoxicillin for heart problems, to prevent chlamydia during pregnancy, to prevent bacterial infection in newborns, or to protect the heart valve after surgical procedures. Amoxicillin can also be used “off-label” to treat anthrax. Amoxicillin should only be used “off-label,” in other words, for purposes not usually specified, if specifically recommended by a healthcare provider.
PACKAGING
Amoxicillin comes in the form of tablets for oral use: 500 mg per tablet, 50 tablets per pack.
Active ingredient:
Amoxicillin.
Excipients:
Potato starch, talc, tween-80 (polysorbate-80,) magnesium stearate.
DOSAGE
Orally, before or after a meal.
Adults and children over 10 years old (with a body weight of more than 40 kg) are prescribed 500 mg 3 times a day; in severe infections – 750-1000 mg 3 times a day.
In acute uncomplicated gonorrhea, 3000 mg is prescribed once for men and twice for women.
In acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (paratyphoid fever, typhoid fever) and biliary tract, with gynecological infectious diseases for adults, 1500-2000 mg 3 times a day or 1000-1500 mg 4 times a day. In severe infections (meningitis, septicemia) adults – up to 6000 mg per day in 3-4 doses. Children – 250-500 mg 3 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the indications and clinical presentation and is usually 5-7 days. With otitis media and similar infections in children, a two-time administration of Amoxicillin is sufficient. In cases of chronic diseases, recurrent infections, severe infections, adults are prescribed 750-1000 mg 3 times a day, children up to 60 mg / kg of body weight per day are divided into 3 doses.
Leptospirosis for adults – 500-7500 mg 4 times a day for 6-12 days.
Listeriosis, adults 500 mg 3 times a day for 6-12 days. Adults with salmonella – 1500-2000 mg 3 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
For the prevention of endocarditis in minor surgical interventions for adults – 3000-4000 mg 1 hour before the procedure. If necessary, a repeated dose is prescribed after 8-9 hours. In children, the dose is halved.
PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug (including other penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems), allergic diseases (including a history), bronchial asthma, hay fever, infectious mononucleosis, lymphocytic leukemia, liver failure, colitis associated with the use of antibiotics, including history, lactation, children under 10 years old with body weight less than 40 kg.
With caution: Pregnancy, allergic reactions, (including a history), a history of gastrointestinal tract diseases, renal failure, and also with a history of bleeding.
Pregnancy and lactation: It is possible to use amoxicillin during pregnancy when the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Amoxicillin is excreted in breast milk with low concentrations. If you need to use the drug during lactation, you should decide on the termination of breastfeeding.
SIDE EFFECTS
Allergic reactions: skin rash, hyperemia, itching, urticaria, erythema, angioedema, rhinitis, conjunctivitis; fever, joint pain, eosinophilia.
From the digestive system: dysbiosis, taste change, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, stomatitis, glossitis, impaired liver function.
From the nervous system: agitation, anxiety, insomnia, ataxia, confusion, behavior change, depression, peripheral neuropathy, headache, dizziness, convulsions.
Laboratory indicators: leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, anemia.
Other: shortness of breath, tachycardia, interstitial nephritis, crystalluria, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, vaginal candidiasis.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.